Toolbar
Filter
Filtering is a key tool for data management, allowing users to quickly find desired data sets based on specific conditions. This document provides a detailed introduction to the filtering functionality, including explanations of operators, field types, condition grouping, and other aspects to help users fully understand and utilize filtering for data analysis and management.
Basic Rules List
Adding Conditions
- Users can set filter rules by clicking the “Add condition” button.
- Each condition consists of three parts: field, operator, and value.
- Supports direct value input or selection from preset options.
Adding Condition Groups
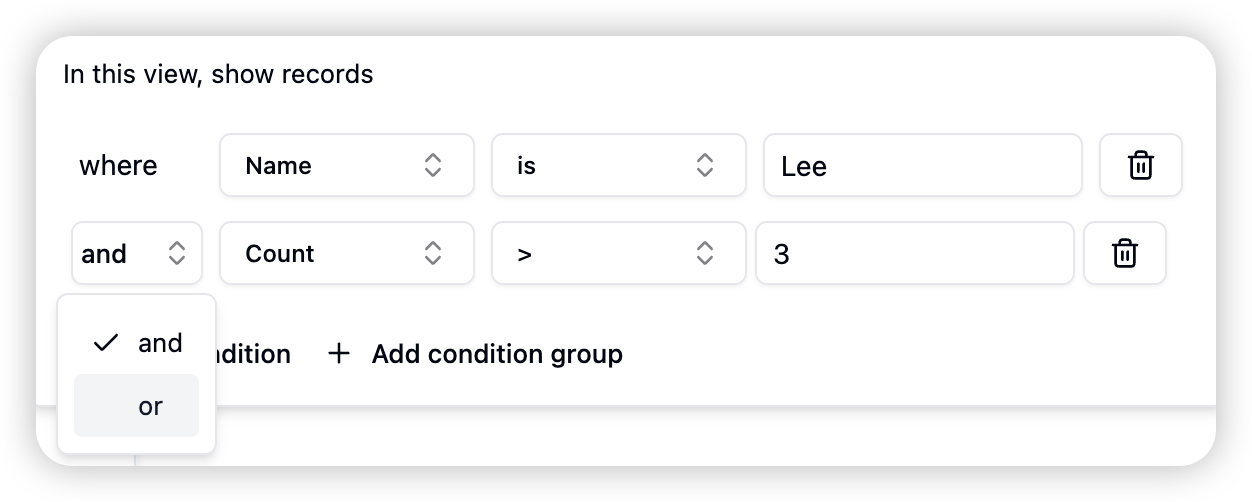
- Through the “Add group” button, users can “create condition groups” using “AND” or “OR” logic to connect conditions.
- Groups can be nested with more groups inside to implement complex filtering logic.
Supported Basic Types and Operators
Text Type Equals, Does not equal, Contains, Does not contain, Is empty, Is not empty Number Type =, ≠, >, ≥, <, ≤, Is empty, Is not empty Date Type Before, After, Between, Equals, Does not equal, Is empty, Is not empty Boolean Field Is, Is not Custom Option Field Equals, Does not equalOperators and Their Input Data Types
- Text operators accept string type data.
- Number operators accept numerical type data.
- Date operators accept date type data.
- Boolean operators require no input, direct selection.
- Custom option operators accept predefined options.
Field Types and Operator Mapping
| Field Type | Supported Operators | Input Data |
|---|---|---|
| Single Line Text | Equals, Does not equal, Contains, Does not contain, Is empty, Is not empty | Text input |
| Long Text | Equals, Does not equal, Contains, Does not contain, Is empty, Is not empty | Text input |
| User | Equals, Does not equal, Contains any, Does not contain any, Is empty, Is not empty | User selection list, and current user |
| Attachment | Is empty, Is not empty | - |
| Multiple Select | Contains any, Contains all, Exactly matches, Does not contain any, Is empty, Is not empty | Option selection list |
| Single Select | Equals, Does not equal, Contains any, Does not contain any | Option selection list |
| Date | Equals, Does not equal, Within, Before, After, On or before, On or after, Is empty, Is not empty | Preset range list, precise date picker |
| Number | =, ≠, >, ≥, <, ≤, Is empty, Is not empty | Number |
| Duration | Equals, Does not equal, Greater than, Greater than or equal to, Less than, Less than or equal to, Is empty, Is not empty | Number |
| Rating | Equals, Does not equal, Greater than, Greater than or equal to, Less than, Less than or equal to, Is empty, Is not empty | Number |
| Formula | Operators determined by result type | Text, Number, Date |
| Rollup | Operators determined by result type | Text, Number, Date |
| Count | Equals, Does not equal, Greater than, Greater than or equal to, Less than, Less than or equal to, Is empty, Is not empty | Number |
| Lookup | Equals, Does not equal, Contains, Does not contain, Contains any, Contains all, Exactly matches, Does not contain any, Is empty, Is not empty | Lookup value selector |
| Created Time | Equals, Does not equal, Within, Before, After, On or before, On or after, Is empty, Is not empty | Preset range list, precise date picker |
| Last Modified Time | Equals, Does not equal, Within, Before, After, On or before, On or after, Is empty, Is not empty | Preset range list, precise date picker |
| Created By | Equals, Does not equal | User selection list, and current user |
| Last Modified By | Equals, Does not equal | User selection list, and current user |
| Auto Number | =, ≠, >, ≥, <, ≤ | Number |
| Button | - | - |
Condition Grouping Functionality
Condition grouping allows users to combine multiple conditions using logical operators (such as “AND/OR”). The core of this functionality lies in its logical flexibility and combinatorial capabilities, enabling users to construct nested logic based on complex requirements for refined data filtering.AND/OR Logic
- AND Logic: All conditions within the group must be satisfied simultaneously to select data.
- OR Logic: Any condition within the group being satisfied is sufficient to select data.
Combination Operations
- Users can create multi-level nested condition groups, with each level defining its own logical relationship.
- Groups can be infinitely nested to achieve extremely complex filtering logic.
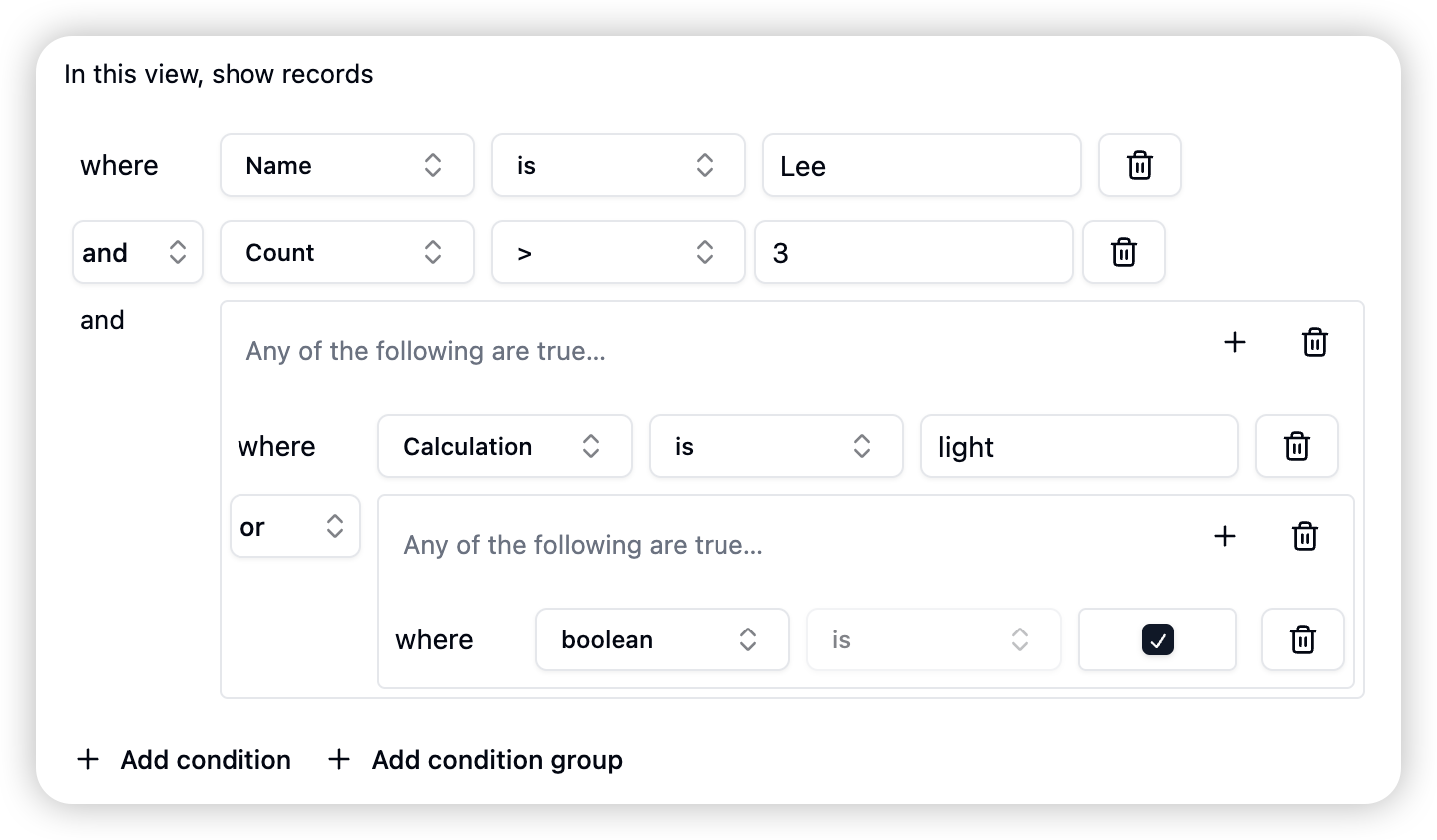
Steps for Using Condition Groups
- Create Group: Users create a new condition group through the interface command.
- Add Conditions: Within the group, users can add multiple filter conditions.
- Select Logic: For conditions within the group, users need to choose “AND” or “OR” logic.
- Nest Groups: Users can continue to create new subgroups inside a group and set conditions and logic for them.
- Optimize Logic: Users can adjust the logical relationships of various conditions and groups as needed to achieve the desired filtering effect.
Example
Suppose a user needs to filter a database to find all records that were “created by a specific user” AND “either modified in the past week OR have a rating above 8”, they can construct the following condition group logic:- Main Group (AND)
- Condition 1: Created By = Specific User (AND)
- Subgroup (OR)
- Condition 2: Last Modified Time = Past Week
- Condition 3: Rating > 8