Table
Overview
Each base can contain multiple tables. A table is a structured data storage method used to store collections of related data within a base.
Each table typically contains multiple rows and columns, where each column represents a field and its attributes, while each row represents a record or data item. Tables are core components of bases, used for collecting, storing, and processing data for subsequent retrieval, manipulation, and base construction.
Teable’s tables are equivalent to tables in a database, a concept that helps understand the differences between Teable and traditional spreadsheets for better mastery of Teable.
Adding Tables
- Enter a specific base
- Click the + button in the directory
- Create a new table
- Import a table from a CSV file
- Import a table from an Excel file
Modifying Table Names
- In the application, double-click the table name in the directory
- Modify the table name
- Click any area outside the input box
Deleting Tables
- Hover over the table in the directory, click the ”…” button to open the menu
- Click the delete button in the menu
Trash
Click the trash button in the upper left of the base to enter the table trash interface and perform the following operations.Table data in the trash can still be accessed by database connections
- Empty trash: Permanently delete all table data
- Restore: Restore tables back to the base
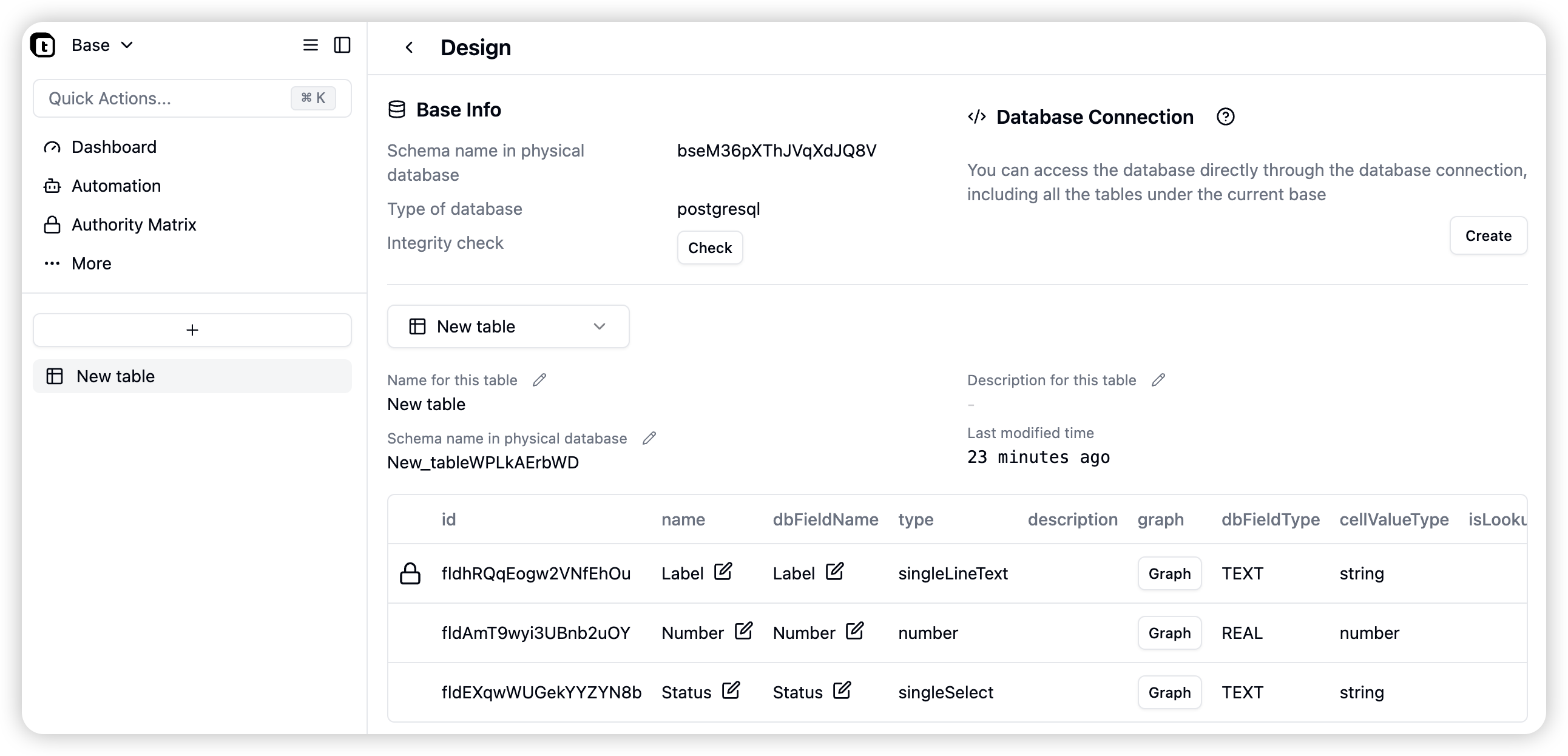
Designing Tables
Click the design button in the menu to enter the table design page, where you can view the table’s basic properties, including: Table Related- Base Schema the table belongs to
- Table name and its name in the physical table
- Table description
- Modification time
- Database connection
- Number of database connections
- id: Field ID
- name: Field name
- dbFieldName: Field name in the physical database
- type: Field type
- description: Field description
- graph: View current field dependencies
- cellValueType: Current field value type
- isLookup: Whether it’s a field looked up from a linked table
- isMultipleCellValue: Whether it’s an array value field
- isComputed: Whether it’s a computed field (record values of computed fields cannot be modified)
- isPending: Whether it’s in calculation
- hasError: Whether there are calculation errors
- notNull: Whether non-null validation is enabled
- unique: Whether unique value validation is enabled
